Additional analysis of NSTX discharges with different collisionality
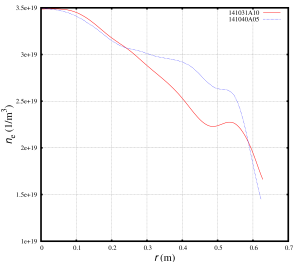
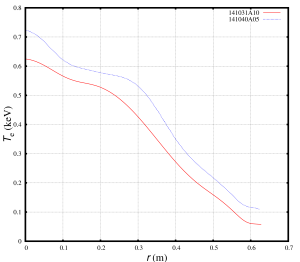
The NSTX discharges 141031 and 141040 have comparable density profiles, but their temperature profiles are distinguishably different:
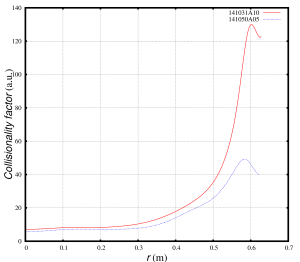
If collisionality is evaluated using the expression , the difference in collisionality between two NSTX discharges is several percents in the plasma core and increases to about 25% at r = 0.5 m. The plasma collisionality in the NSTX discharge 141031 is above the collisionality in the discharge 141040 for all radii:
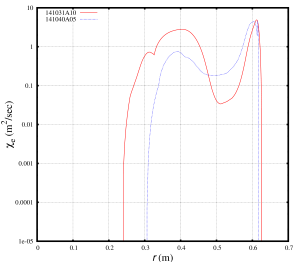
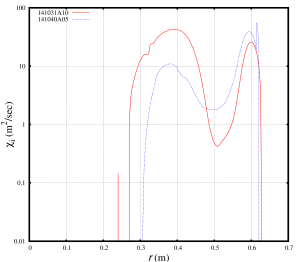
Being tested directly in the MMM8.1 model, the anomalous diffusivities for the NSTX discharge 141031 are found above the anomalous diffusivities for the NSTX discharge 141040. This statement is not true in the H-mode pedestal region where the results from anomalous transport models are not reliable. Smaller anomalous diffusivities are likely to result in better energy confinement times. The predicted energy confinement for the NSTX discharge 141040 is likely to be better than the predicted energy confinement for the NSTX discharge 141031. This is in agreement with the experimental trends for these two discharges.
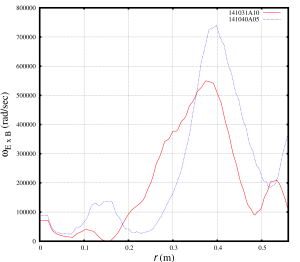
The observed dependence of the anomalous diffusivities on the collisionality is not necessary comes from the model, but might be associated with the differences in other profiles and plasma parameters that are difficult to maintain constant between discharges. In particular, in order to isolate the collisionality and ExB flow shear effects, the ExB flow shear profiles were set to zero in these tests. The ExB flow shear profiles between the two NSTX discharge are different:
The ExB flow shear rates for the NSTX discharge 141031 are above the ExB flow shear rates for the discharge 141040 in the plasma region from r=0.18m to r=0.5m and below the ExB flow shear rates in the outer plasma region from r=0.8m. In particular, the ExB flow shear rates are large in the region from r=0.35m to r=0.45m. While neglected in the direct tests with the MMM8.1 model, the ExB flow shear rates were used in the TRANSP predictive simulations last week.
In order to eliminate possible effects from other plasma parameters that are different for the NSTX discharges 141031 and 141040, independent collisionality scans for each discharge are necessary.